Forest Industries Keep America Working
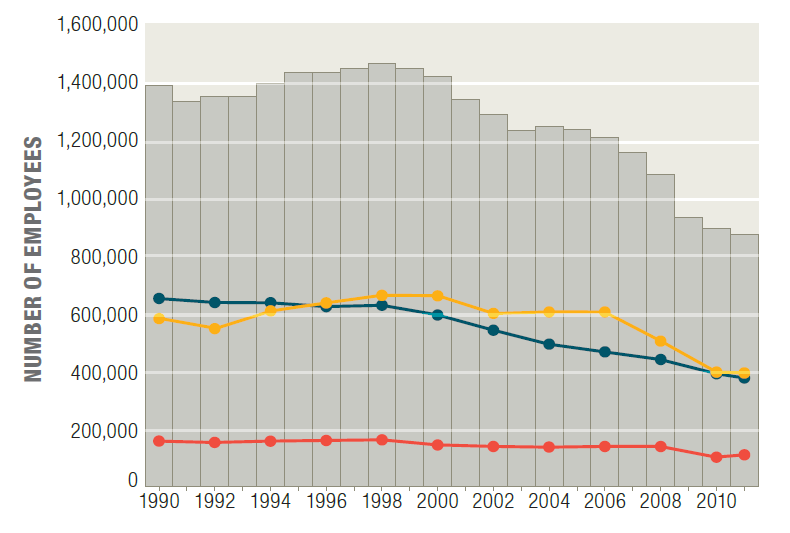
Forest industries are a major contributor to the US economy, by providing jobs from forests to showrooms. The economic benefits of the industry are felt throughout the nation, but each region of the country relies on different components of the industry to varying degrees: from softwood lumber and plywood production in the west to hardwood manufacturing in the east.
The forest industry is composed of many different occupations, from natural resource professionals working in the field, to production workers in mills and factories, to statistics and financial experts working in office settings. Forestry and logging workers study the timber resource and deliver raw materials to wood products facilities, while wood and paper mill employees work in the manufacturing sector. The common thread among these jobs is the resource they are ultimately tied to — trees harvested from the Nation's forests.